当客户端输入 mysql -h x.x.x.x -u root -p 时,服务端在做什么(中)¶
Conventions
- 每一个代码块的顶部都有它所属的文件(相对)路径,如果代码块属于某个函数(方法),那么顶部会有函数(方法)的声明。
- 代码块中的对象,如果很重要,会在行尾补充该对象的声明。
- 我使用的MySQL 版本是 8.0.41。你看到这篇时,可能有了更新的版本,比如 8.0.42,区别不大的。
身份认证¶
| sql/sql_connect.cc | |
|---|---|
上一篇结尾,我们讲到 thd_prepare_connection 函数会验证用户名和密码。
thd_prepare_connection 方法很简短,一眼就看到第 893 行的 login_connection 是关键。
login_connection 方法也很简短,但如果每个方法都完整列出来,代码块会占很大的篇幅,所以接下来的几个方法,直接展示调用链,因为真的不重要,重要的肯定会贴出来的。
| sql/sql_connect.cc | |
|---|---|
| sql/sql_connect.cc | |
|---|---|
| sql/auth/sql_authentication.cc | |
|---|---|
| sql/auth/sql_authentication.cc | |
|---|---|
- st_mysql_auth *auth
login_connection -> check_connection -> acl_authenticate -> do_auth_once -> authenticate_user 这么一路调用下来,走到上面这行停住。
auth 是指向结构类型的指针,表示身份认证插件,authenticate_user 是该结构的成员,对应类型 int (*)(MYSQL_PLUGIN_VIO *vio,MYSQL_SERVER_AUTH_INFO *info),这是指向身份认证函数的指针类型。
不同的身份认证插件会有不同的实现,我们只看默认插件 caching_sha2_password 的实现。caching_sha2_password 在文件 sql/auth/sha2_password.cc 中。caching_sha2_password_authenticate 函数是身份认证函数在该插件中的具体实现,也就是说 authenticate_user 指向了这个函数,所以接下来我们会看这个函数。
Tip
MySQL 有 3 种身份认证插件,分别是 mysql_native_password、sha256_password、caching_sha2_password。
握手¶
static int caching_sha2_password_authenticate(MYSQL_PLUGIN_VIO *vio,
MYSQL_SERVER_AUTH_INFO *info) {}
caching_sha2_password_authenticate 这个函数比较长,就不贴出来了。这个函数中我认为我们要关注的是两件事,一件是服务端与客户端的握手,另一件就是验证密码。下面我们先看握手,验证密码得放到下一篇。
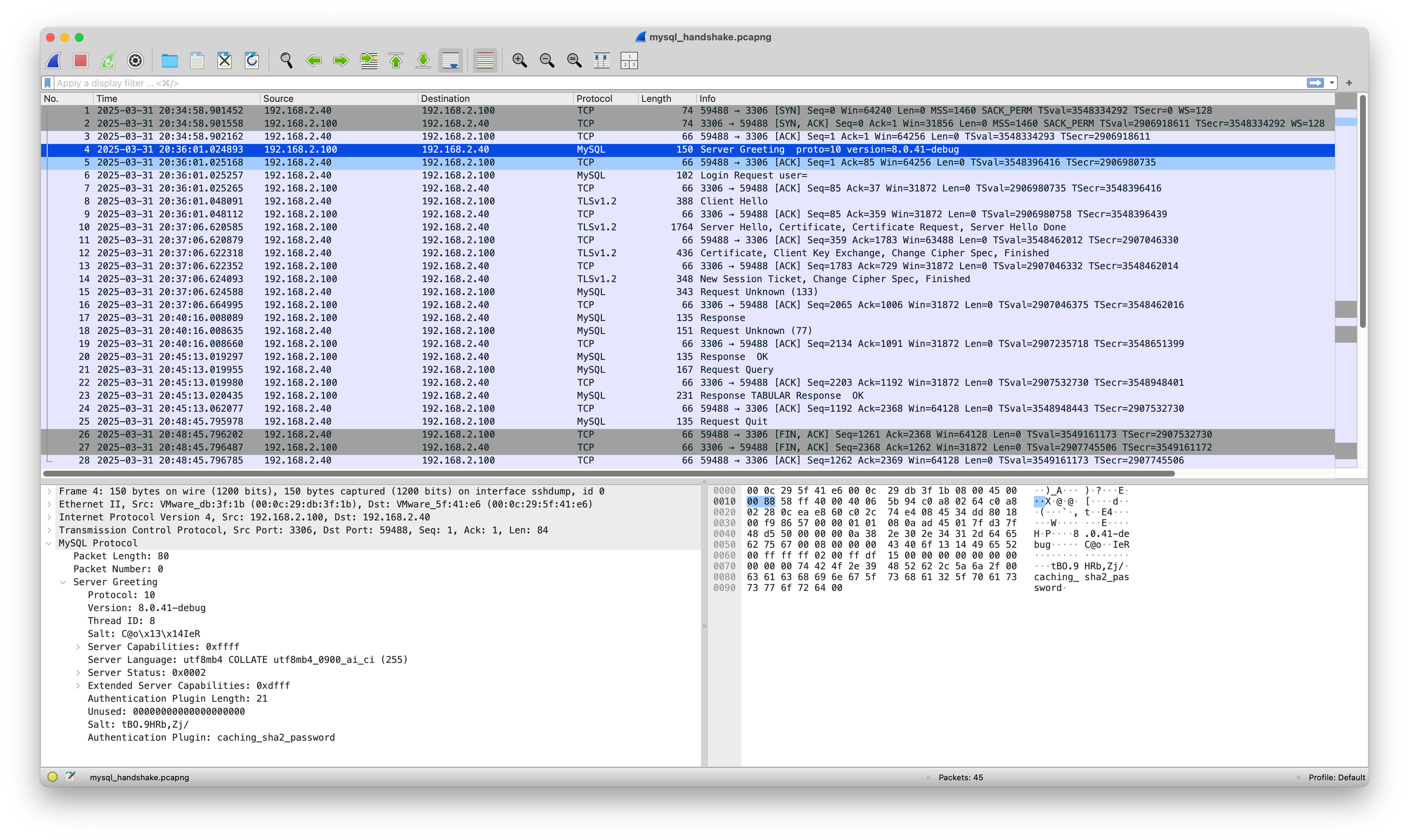
TCP 的握手大家肯定都听过,这儿讲的是 TCP 握手之后,MySQL 实现的服务端与客户端的握手。下面我们通过 Wireshark 查看这个过程。
Tip
单击图片可以放大图片,看得更清楚。
1、2、3 号包是 TCP 的握手,4 号和 6 号是 MySQL 的握手。
4 号包是 MySQL 服务端发出的,说明握手是服务端发起。上图中左下方有包内容,可以看到服务端通过握手传递了版本号、协议版本、盐、身份认证的插件等信息,对应下面函数:
| sql/auth/sha2_password.cc static int caching_sha2_password_authenticate(MYSQL_PLUGIN_VIO *vio, MYSQL_SERVER_AUTH_INFO *info) | |
|---|---|
write_packet 是指向函数的指针,指向下面的函数 server_mpvio_write_packet。
关键在第 3241 行 send_server_handshake_packet 函数,函数名翻译成中文就是发送服务端握手包,对应 Wireshark 截图中的 4 号包。
详解服务端握手包¶
---
title: "MySQL Server Greeting Packet"
---
packet-beta
0-23: "Packet Length: 80"
24-31: "Packet Number: 0"
32-39: "Protocol: 10"
40-143: "Version: 8.0.41-debug"
144-175: "Thread ID: 8"
176-247: "Salt: C@o\\x13\\x14IeR"
248-263: "Server Capabilities: ffff"
264-271: "Server Language: utf8mb4"
272-287: "Server Status: 0002"
288-303: "Extended Server Capabilities: dfff"
304-311: "Authentication Plugin Length: 21"
312-391: "Unused: 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00"
392-495: "Salt: tB0.9HRb,Zj/"
496-671: "Authentication Plugin: caching_sha2_password"上面这张图是 4 号包的样子,我们按照代码一个一个过。
| sql/auth/sql_authentication.cc | |
|---|---|
1600 1601 1602 1603 1604 1605 1606 1607 1608 1609 1610 1611 1612 1613 1614 1615 1616 1617 1618 1619 1620 1621 1622 1623 1624 1625 1626 1627 1628 1629 1630 1631 1632 1633 1634 1635 1636 1637 1638 1639 1640 1641 1642 1643 1644 1645 1646 1647 1648 1649 1650 1651 1652 1653 1654 1655 1656 1657 1658 1659 1660 1661 1662 1663 1664 1665 1666 1667 1668 1669 1670 1671 1672 1673 1674 1675 1676 1677 1678 1679 1680 1681 1682 1683 1684 1685 1686 1687 1688 1689 1690 1691 1692 1693 1694 1695 1696 1697 1698 1699 1700 1701 1702 1703 1704 1705 1706 1707 1708 1709 1710 1711 1712 1713 1714 1715 1716 1717 1718 1719 1720 1721 1722 1723 1724 1725 1726 1727 1728 1729 1730 1731 1732 | |
1606 行声明并初始化了一个缓冲区 buff,1608 行 end 指向缓冲区 buff。
接着,就是往缓冲区中写入 Protocol、Version、Thread ID等 4 号包所示的字段值。
1611 行写入 Protocol,占 1 个字节。
1697 行写入 Version,占用字节数不固定,以 0 结尾,对于当前例子是 8.0.41-debug 12 字节外加结尾的 0 共占 13 个字节。
1700 行写入 Thread ID,占 4 个字节,当我们使用 mysql 命令登录时,欢迎语中会显示这个值。
1708 行写入 Salt,占 8 个字节,这是整个盐的前面部分。
1710 行写入 0,占 1 个字节。
1712 行写入 Server Capabilities,占 2 个字节,每一位都是一个标识位,表示服务端支持的功能。
1714 行写入 Server Language,占 1 个字节。
1715 行写入 Server Status,占 2 个字节。
1716 行写入 Extended Server Capabilities,占 2 个字节,每一位都是一个标识位,表示服务端支持的功能。
1717 行写入 Authentication Plugin Length,占 1 个字节,表示盐的总字节数。
1720 行写入 Unused,占 10 个字节,全部以 0 填充。
1723 和 1724 行写入 Salt,占 13 个字节,与 1708 行的盐拼在一起,是完整的盐。
1726 和 1727 行写入 Authentication Plugin,占用字节数不固定,以 0 结尾,对于当前例子是 caching_sha2_password 21 字节外加结尾的 0 共占 22 个字节。
1729 行会计算 buff 缓冲区的字节数,作为 Packet Length,占用 3 个字节,外加 1 个字节的 Packet Number。这样,整个服务端握手包就生成好了。
| sql/auth/sha2_password.cc | |
|---|---|
完成发送服务端握手包后,函数返回到 caching_sha2_password_authenticate。接着,往下走到第 962 行的 read_packet 函数,这也是指向函数的指针,指向 sql/auth/sql_authentication.cc 的 server_mpvio_read_packet 函数,这个函数稍稍有点长,不贴出来了。我们只需要关心,在该函数中调用了下面的 parse_client_handshake_packet 函数,即解析客户端握手包,这个包对应 Wireshark 截图中的 6 号包。
static size_t parse_client_handshake_packet(THD *thd, MPVIO_EXT *mpvio,
uchar **buff, size_t pkt_len) {
// ignore
/*
If client requested SSL then we must stop parsing, try to switch to SSL,
and wait for the client to send a new handshake packet.
The client isn't expected to send any more bytes until SSL is initialized.
*/
if (protocol->has_client_capability(CLIENT_SSL)) { // line 2882
// ignore
if (sslaccept(*(context.get()), protocol->get_vio(), // line 2900
protocol->get_net()->read_timeout, &errptr)) {
DBUG_PRINT("error", ("Failed to accept new SSL connection"));
return packet_error;
}
DBUG_PRINT("info", ("Reading user information over SSL layer"));
int rc = protocol->read_packet(); // line 2907
pkt_len = protocol->get_packet_length();
}
// ignore
char *user = get_string(&end, &bytes_remaining_in_packet, &user_len); // line 2999
// ignore
passwd =
get_length_encoded_string(&end, &bytes_remaining_in_packet, &passwd_len); // line 3011
在解析客户端端握手包过程中,如果发现客户端支持 TLS(第 2882 行),那么会进行 TLS 握手(第 2900 行),TLS 握手完成后客户端会发送用户名和密码,服务端阻塞读取(第 2907 行),然后解析(第 2999 和 3011 行)得到用户名和密码。
小结¶
MySQL 服务端和客户端在 TCP 握手完成后,并没有立刻进行 TLS 握手,而是先做了基础信息的交换,比如版本号、是否支持 TLS 等信息,这是 MySQL 自身实现的握手,如果支持 TLS,那么才进行 TLS 握手,全部完成后,客户端发送用户名和密码,服务端接收到后解析。
下一篇,讲讲服务端如何验证用户名和密码。